A native app can be directly installed to your smart phone and in most cases, can work without internet connectivity, depending on the nature of the app. A web app on the other hand works via web browser on the smartphone and needs either your mobile signal or Wi-fi to function.
Why Native Apps?
Native apps are the ones which can be downloaded through an application store on your phone. These apps are coded specifically for a particular device. They can either be paid or free. Native apps can make use of any of the features on your phone like the camera, the GPS (like Google maps).
Here are some of the advantages of creating native apps: –
1. Aspect Ratio
Apps which are developed keeping tablets in mind won’t be that compatible for smart phones and vice versa. So, the principle of one size fits all does not apply in this situation. Not only do the aspect ratios vary from one device to another, but the DPI (dots per inch) also differ. These things change the look and appearance of the app on different devices.
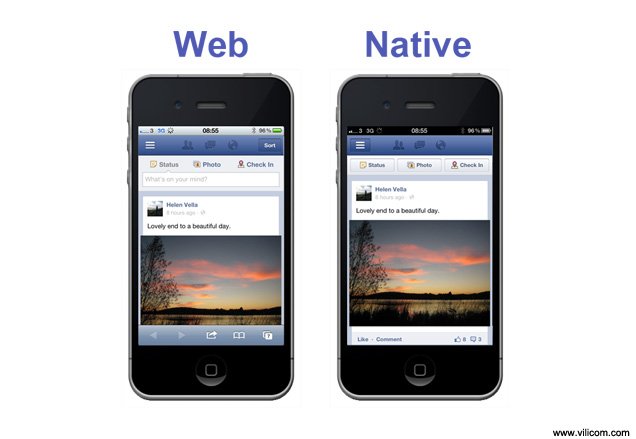
Take for example, Facebook or Twitter. You don’t even need to look twice to say that in case of both of them, their apps and desktop sites look worlds apart. If apps are developed using objective C or Java the resolution, size and orientation can be controlled skillfully.
2. User Feels at Home
Really, who wouldn’t want to? With a native app, it feels like it belongs in your device and does not look out of place. With native apps, users register icons and buttons related to it very quickly.
3. Simple Navigation
While using a native app on your any of your personal devices, you expect specific kind of functions and features like zoom and multi-touch. Not only that, even the location of ‘back’ option varies in different devices. These functions can be accessed with a lot of ease in native apps. Native apps without any difficulty respond to user gestures such as swipes and pinches.

4. Easy Access to Other Features
Since native apps are developed specifically for that device, they can easily make use of other features of that particular device. IOS and Android devices all have pedometers, GPS, cameras and a dozen other features. With native apps, you get to use these features and it is basically a cakewalk for developers to add these features to the app. With web apps there’s the constant struggle to access many of these features and implementing them is a gigantic task.
5. Integration with Device Hardware
Web apps might be becoming more refined in terms of design, but they are still miles away from figuring out how native apps communicate with different kinds of device hardware components. Native apps can fluidly communicate with Bluetooth, USB, cameras, and GPS. In addition to this ability to communicate with a device’s hardware, native apps can also link with other apps present on a user’s device.
6. Internet Connectivity
The biggest boon of all, it is not necessary that a native app on your phone requires internet connectivity. You can navigate through an app without having to rely on WiFi/Mobile Data, by using its offline mode.
Why Webapps?
Now that some of the advantages of native apps have been gauged, have a look at what web apps have to offer: –
1. Low Maintenance Cost
Let’s face it, there are so many start ups which are mostly short on capital in the beginning. But at the same time, their business can’t do without a website. So, going for a mobile website covers all bases since setting up an app requires both time and money. You do not need to reformat and duplicate content or add features twice for different kinds of devices.
2. Compatibility
They work smoothly on all devices! Be it iOS or Android. Unlike native apps, which have to be developed and tweaked according to different kinds of devices like phone, tablets and PCs. whereas, a mobile website needs to be only created once. One size fits all definitely applies in this case.
3. Faster Loading Speed
No one wants to go through the horror of opening a desktop friendly page, on a mobile phone. It is the ultimate test of a user’s patience especially since our average attention span has greatly reduced. A mobile website increases loading speed and this in turn results in a better user experience. Since the downloading speed increases, at the same time it uses less bandwidth.

4. Easy Updates
You do not need to download and install updates like you are required to in native apps. The developers themselves update mobile websites if there are changes to be made in content or design, and then next time a user navigates the page, those changes are visible, without the user having to do anything to see those updates.
5. Immediately Available
A mobile website is just a browser away for a user to access across a range of devices (iPhone, Android, BlackBerry, etc). Native apps however, require the user to first download and install the app from an app store before the content or application can be viewed. Suppose the user does not want to download the app, this becomes the first barrier between a business and a consumer. The reach becomes limited.
6. Greater Reach
A mobile website has a far higher reach in terms of the target audience in comparison to a native app. That is because it is available on all platforms; it can be easily shared by users and also increases visibility on search engines.
As mobile is still somewhat a new platform, the perpetual debate about “app v/s web” has become a very real concern for businesses and organizations looking to establish their presence on mobile platforms. If your business’ mobile goals are mainly market-driven, or if the aim is to deliver content and create a far-reaching mobile presence that can be effortlessly shared between users and found on search engines, in that case, a mobile website is a rational decision. Then again, if your goal is interactively engaging with users, or providing them an application that needs to look more like a computer program than a website, an app is probably better in this case.






